What factors affect the lifespan of graphite electrodes, and how
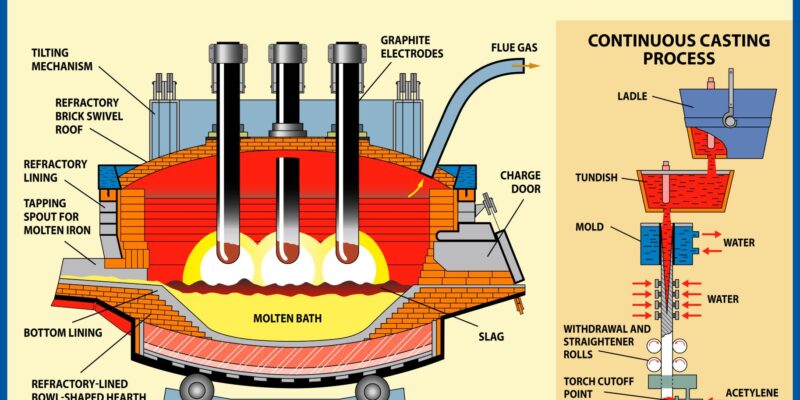
1. Operating Conditions:
Extreme temperatures, high electrical currents, and chemical reactions in the furnace environment can all impact electrode lifespan. Manufacturers need to design electrodes capable of withstanding these harsh conditions without significant degradation.
2. Electrode Quality:
The quality of the raw materials used in electrode manufacturing, as well as the production process itself, greatly influence electrode durability. Ensuring consistent material composition, proper compaction, and minimal impurities during manufacturing can enhance electrode lifespan.
3. Furnace Design:
The design and operation of the electric arc furnace (EAF) or other industrial equipment where graphite electrodes are used play a significant role in electrode lifespan. Factors such as furnace geometry, electrode positioning, and cooling systems can affect electrode wear and performance.
4. Electrode Handling and Installation:
Improper handling, storage, or installation of graphite electrodes can cause damage and shorten their lifespan. Manufacturers and operators must follow best practices for handling and installing electrodes to minimize the risk of mechanical damage or breakage.
5. Electrode Coating and Surface Treatment:
Applying protective coatings or surface treatments to graphite electrodes can improve their resistance to oxidation, thermal shock, and chemical attack. Manufacturers may optimize electrode coatings to enhance durability and performance in specific furnace environments.
6. Maintenance Practices:
Regular maintenance and inspection of electrodes and furnace components can help identify issues early and prevent premature electrode failure. Implementing proactive maintenance schedules, such as routine electrode dressing or monitoring electrode wear, can extend their lifespan.
By addressing these factors and continually refining electrode design, materials, and manufacturing processes, manufacturers can optimize the durability and performance of graphite electrodes in industrial applications, ultimately reducing downtime and maintenance costs for steelmakers and other users.





