Graphite Electrode
Graphite electrodes are mainly used in electric arc furnace. They are presently the only products available that have the high levels of electrical conductivity and the capability of sustaining the extremely high levels of heat generated in EAF. Graphite electrodes are also used to refine steel in ladle furnaces and in other smelting processes. Graphite electrodes are divided into 4 Types: RP Graphite electrodes, HP Graphite electrodes, SHP Graphite electrodes, UHP Graphite electrodes.
- Product Details
Graphite Electrode Soldering Iron
Graphite electrode is nothing more than a sharp graphite rod, taken from a pile, subject to a support conductor of the current, copper tube, and at a reasonable distance a plastic handle, PVC tube. The handle should be far enough away so that it does not reach so much heat to soften it. Anyway it is clear that PVC is the worst plastic that can be used for this but it was there.
This is a sheet metal welder for almost any metal. It does not require input of material and practically does not admit it unless they are very thin rods. It is not about electric arc welding. What melts the metal is the graphite tip that shortly turns to bright white. What is heated by the current is graphite, not metal, Graphite electrode because the first one has a much greater resistance and dissipates most of the power. It is important that the graphite tip is sharp for two reasons:
The finer the point of contact between the material and the tip more resistance to current and more temperature reach. If it is too thick, heat is transmitted easily from the tip to the soldering iron and a large part of it dissipates without reaching the necessary temperature. The soldering iron only works if it concentrates most of the power at the point to be soldered. Everything has to be thought for that.
The truth is that to have been done in 10 minutes, nothing else came up with the idea, it was pretty good. The way to hold the Graphite electrode was the idea of a friend and is interesting for its simplicity. It involves making two cuts on the edge of the tube longitudinally dividing it into 4 more or less equal parts. Two of them are eliminated and the tube is left with two tabs. Each one is tightened with pliers to give it a round shape and it adapts to the bar and then approaches each other. You are looking for a large brass nut that snaps into place and, without the rod; you turn the nut with force, making a thread in the copper. Then open, put the bar and do the same again and is perfectly subject. This system allows changing the bar quickly, adjusting its position, and providing a good electrical contact.
Graphite electrode is mainly used in electric arc furnace. They are presently the only products available that have the high levels of electrical conductivity and the capability of sustaining the extremely high levels of heat generated in EAF. Graphite electrodes are also used to refine steel in ladle furnaces and in other smelting processes. Graphite electrodes are divided into 4 Types: RP Graphite electrodes, HP Graphite electrodes, SHP Graphite electrodes, UHP Graphite electrodes.
Diameter and length for all grades:
|
Diameter mm |
Length mm |
|||||
|
Nominal Diameter |
Actual Diameter |
Nominal Length |
Allowance |
|||
|
mm |
inch |
Max |
Min |
mm |
Standard |
Short |
|
200 |
8 |
205 |
200 |
1800 |
± 100 |
-275 |
|
250 |
10 |
256 |
251 |
1800 |
||
|
300 |
12 |
307 |
302 |
1800/2000 |
||
|
350 |
14 |
357 |
352 |
1800/2000 |
||
|
400 |
16 |
409 |
403 |
1800/2000 |
||
|
450 |
18 |
460 |
454 |
2100/2400 |
||
|
500 |
20 |
511 |
505 |
2100/2400 |
||
|
550 |
22 |
562 |
556 |
2100/2400 |
||
|
600 |
24 |
613 |
607 |
2400/2700 |
||
|
650 |
26 |
663 |
657 |
2400/2700 |
||
|
700 |
28 |
714 |
708 |
2500/2700 |
||
Machining Dimension of Electrode and Nipple:
|
Applicable |
Dia. mm |
IEC code |
Nipple |
Socket |
||
|
Large Dia. mm |
Length mm |
Small Dia. mm |
Socket Depth mm |
|||
|
UHP SHP HP RP |
250 |
155T3N |
155.57 |
220.00 |
147.14 |
116.00 |
|
300 |
177T3N |
177.16 |
270.90 |
168.73 |
141.50 |
|
|
350 |
215T3N |
215.90 |
304.80 |
207.47 |
158.40 |
|
|
400 |
215T3N |
215.90 |
304.80 |
207.47 |
158.40 |
|
|
400 |
241T3N |
241.30 |
338.70 |
232.87 |
175.30 |
|
|
450 |
241T3N |
241.30 |
338.70 |
232.87 |
175.30 |
|
|
450 |
273T3N |
273.05 |
355.60 |
264.62 |
183.80 |
|
|
500 |
273T3N |
273.05 |
355.60 |
264.62 |
183.80 |
|
|
500 |
298T3N |
298.45 |
372.60 |
290.02 |
192.20 |
|
|
550 |
298T3N |
298.45 |
372.60 |
290.02 |
192.20 |
|
|
UHP SHP HP RP |
200 |
122T4N |
122.24 |
177.80 |
115.92 |
94.90 |
|
250 |
152T4N |
152.40 |
190.50 |
146.08 |
101.30 |
|
|
300 |
177T4N |
177.80 |
215.90 |
171.48 |
114.00 |
|
|
350 |
203T4N |
203.20 |
254.00 |
196.88 |
133.00 |
|
|
400 |
222T4N |
222.25 |
304.80 |
215.93 |
158.40 |
|
|
400 |
222T4L |
222.25 |
355.60 |
215.93 |
183.80 |
|
|
450 |
241T4N |
241.30 |
304.80 |
234.98 |
158.40 |
|
|
450 |
241T4L |
241.30 |
355.60 |
234.98 |
183.80 |
|
|
500 |
269T4N |
269.88 |
355.60 |
263.56 |
183.80 |
|
|
500 |
269T4L |
269.88 |
457.20 |
263.56 |
234.60 |
|
|
550 |
298T4N |
298.45 |
355.60 |
292.13 |
183.80 |
|
|
550 |
298T4L |
298.45 |
457.20 |
292.13 |
234.60 |
|
|
600 |
317T4N |
317.50 |
355.60 |
311.18 |
183.80 |
|
|
600 |
317T4L |
317.50 |
457.20 |
311.18 |
234.60 |
|
|
650 |
355T4N |
355.60 |
457.20 |
349.28 |
234.60 |
|
|
650 |
355T4L |
355.60 |
558.8 |
349.28 |
285.40 |
|
|
700 |
374T4N |
374.65 |
457.20 |
368.33 |
234.60 |
|
|
700 |
374T4L |
374.65 |
558.80 |
368.33 |
285.40 |
|
Graphite electrodes uses
Graphite electrodes are used primarily in electric arc furnace steel manufacturing. Graphite electrodes can provide high levels of electrical conductivity and capability of sustaining the extremely high levels of generated heat. Graphite electrodes are also used in the refinement of steel and similar smelting processes.
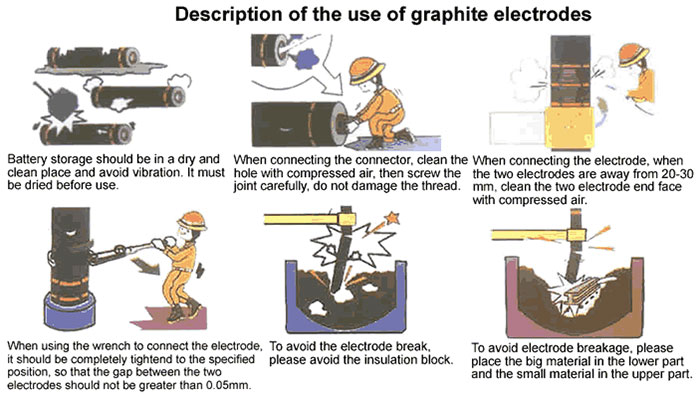
1. The electrode holder should be held in the place beyond the security line of the top electrode; otherwise the electrode would be easily broken. The contact surface between the holder and the electrode should be cleaned up regularly to maintain a good contacting. The cooling jacket of the holder shall be avoided from water leakage.
2. Identify the reasons if there is gap in the electrode junction, do not use the muntil the gap is eliminated.
3. If there is falling off of nipple bolt when connecting electrodes, it is necessary to complete the nipple bolt.
4. The application of electrode should avoid of tilting operation, particularly, the group of connected electrodes should not be put horizontally so as to prevent from breaking.
5. When charging materials to the furnace, the bulk materials should be charged to the place of the furnace bottom, so as to minimize the impact of the large furnace materials on the electrodes.
6. The large pieces of insulation materials should be avoided of stacking on the bottom of the electrodes when smelting, so as to prevent from affecting the electrode use, or even broken.
7. Avoid of collapsing the furnace lid when rising or dropping the electrodes, which may result in electrode damage.
8. It is necessary to prevent the steel slag from splashing to the threads of the electrodes or nipple stored in the smelting site, which my damage the precision of the threads.
Related Products
 Carbon Electrode
Carbon electrode are applied for the production of silicon metal as they have peculiar...
Carbon Electrode
Carbon electrode are applied for the production of silicon metal as they have peculiar...
 Pre-baked Anode Block
Anodes are large carbon blocks which are used to conduct electricity during the aluminium...
Pre-baked Anode Block
Anodes are large carbon blocks which are used to conduct electricity during the aluminium...
 RP Graphite Electrode
Physical & Chemical Properties of RP Graphite Electrodes...
RP Graphite Electrode
Physical & Chemical Properties of RP Graphite Electrodes...









